Consider installing Docker and running PostgreSQL from a Docker container. PostgreSQL is an advanced object-relational database management system that has gained significant popularity. Leveraging Docker, we can swiftly deploy a fully functional instance of PostgreSQL in just a few minutes.
Docker documentation. PostgreSql documentation.
Used:
| Docker | PostgreSQL | Mac OS |
To get started, there are a few essential steps you need to execute:
- Install Docker on macOS, which will allow you to manage and run containerized applications efficiently.
- Deploy a PostgreSQL image from the Docker Hub or any other reliable source. This image will serve as the foundation for your PostgreSQL database.
- Once the PostgreSQL image is successfully deployed, create the necessary databases, tables, and test records to suit your application’s requirements.
- Establish a connection to the PostgreSQL database, enabling your application to interact with the data stored within it.
By following these steps, you can effectively set up Docker, deploy a PostgreSQL image, configure your database structure, and establish a connection for seamless communication between your application and the PostgreSQL database.
Installation and the first steps of Docker described earlier: here. In short, you need to have an account at Docker Hub, download and install the app: Docker Desktop, log in through the terminal.
When Docker is installed and ready to go, prepare a PostgreSql image.
To save data when restarting the container with our database image, it is necessary to create a volume
docker volume create --name vol_1 docker volume ls CAB-WSM-0001037:~ ttt$ docker volume ls DRIVER VOLUME NAME local d67ec8a59da03121046c25a5fd7454417f3d2009d2125a39e4eae1106a7bdcc5 local vol_1 |
create – create a new volume
–name – key “volume name”
ls – returns all Docker volumes
docker run --rm --name postgresql-save -e POSTGRES_PASSWORD=mypassword -d -p 5400:5432 -v vol_1:/var/lib/postgresql/data postgres docker container ls CONTAINER ID IMAGE COMMAND CREATED STATUS PORTS NAMES 51a711b63bfd postgres "docker-entrypoint.s…" About an hour ago Up About an hour 0.0.0.0:5400->5432/tcp postgresql-save d755f0eb4ba2 thajeztah/pgadmin4 "python ./usr/local/…" About an hour ago Up About an hour 0.0.0.0:5050->5050/tcp dreamy_lamarr |
run – running a Docker container
–rm – automatically removes the container if it already exists
–name postgresql-save – set up name
-e POSTGRES_PASSWORD=mypassword – password for DB
-d – backgraound process without locking the command line in the terminal
-p 5400:5432 – set up out port
-v vol_1:/var/lib/postgresql/data – storage of data during content restarts
postgres – the name of the Docker image. You can specify the version
Stop the container
docker container stop postgresql-save |
To connect and work with PostgreSql, you can install the pgAdmin graphical client directly from Docker:
docker run --rm -p 5050:5050 thajeztah/pgadmin4 NOTE: Configuring authentication for DESKTOP mode. pgAdmin 4 - Application Initialisation ====================================== Starting pgAdmin 4. Please navigate to http://0.0.0.0:5050 in your browser. |
IP on MacOs terminal:
ipconfig getifaddr en0 |
You can now connect to PostgreSql.
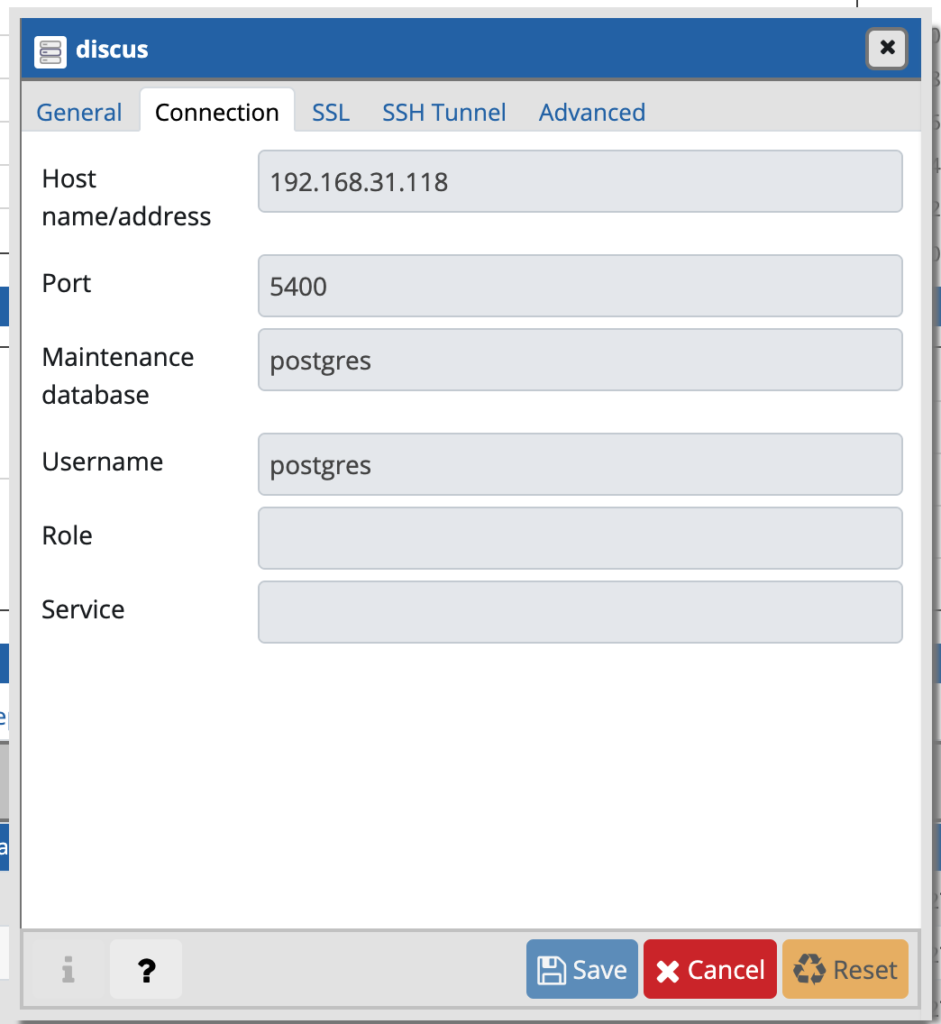
PyCharm with Database plugin
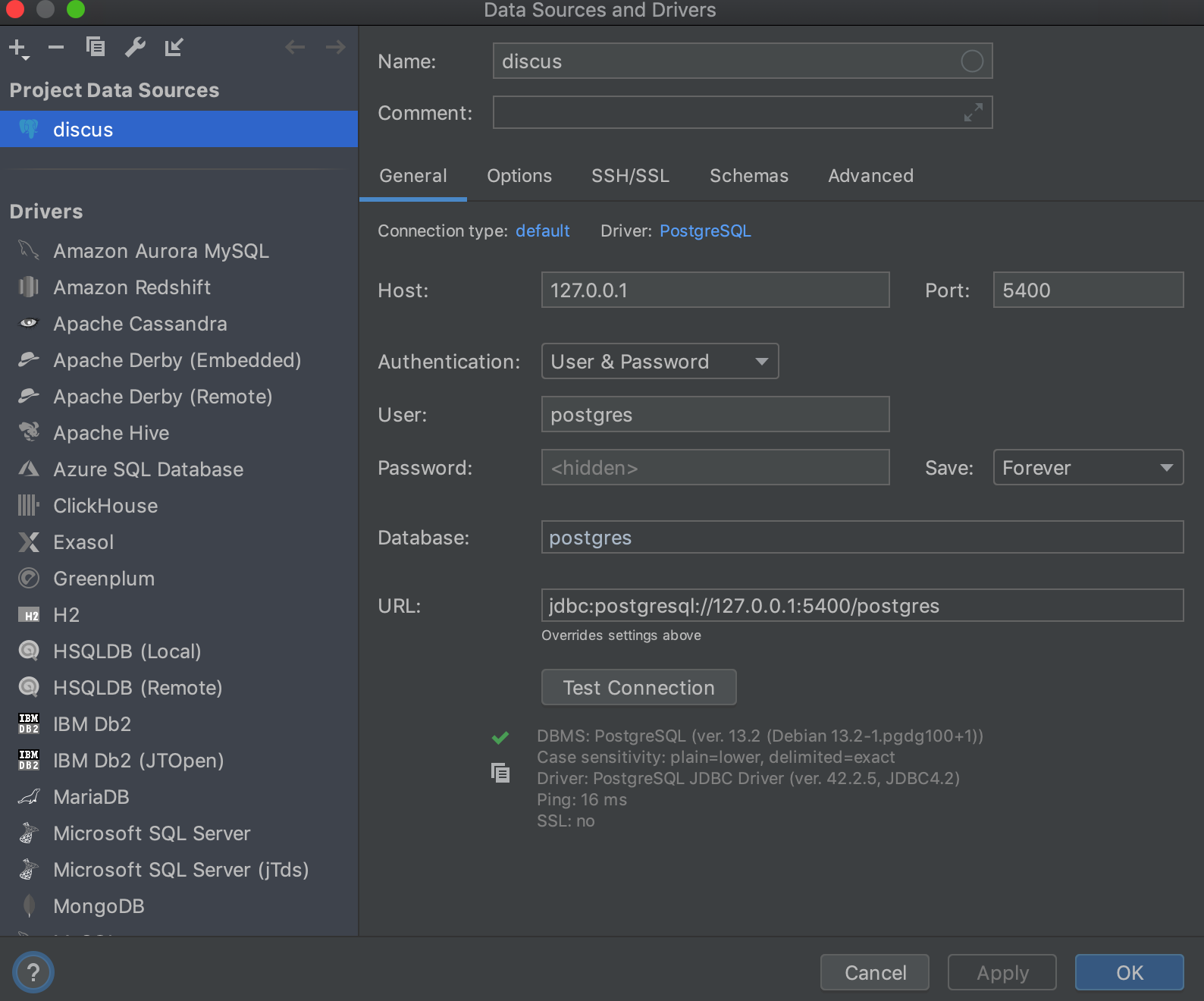
Now, after stopping the container, you can easily start it again, knowing that all your data will be safely preserved. Docker containers are designed to retain data even when stopped or restarted. This means that when you restart the container, it will resume from its previous state, including all the data you had stored within it.
Thanks to Docker’s data persistence feature, you can confidently stop and start your container without any concerns about losing your valuable data. Rest assured that your information will be saved, allowing you to seamlessly continue working with your PostgreSQL database.
docker container stop postgresql-save docker run --rm --name postgresql-save -e POSTGRES_PASSWORD=mypassword -d -p 5400:5432 -v vol_1:/var/lib/postgresql/data postgres |